|
What's New?
|
Some interesting Highlights and interesting facts in telecommunications history are as follows:
- 1837: Samuel Morse develops the electrical telegraph and signaling system. Embarrassingly, he couldn’t get it to work during the unveiling demonstration!
- 1849: Antonio Meucci invents the first device to electronically transmit the human voice (i.e., phone). It flopped because to hear, users had to put the receiver in their mouth.
- 1866: First transatlantic telecommunication is made.
- 1876: Alexander Bell and Elisha Gray independently invent the telephone. Although Gray filed his patent application first, bad legal advice and a clerical error led him to withdraw his application and the patent was awarded to Bell.
- 1878: First commercial telephone service set up in New Haven, Connecticut (home of Yale University) and the following year in London.
- 1901: Guglielmo Marconi positions himself to win the 1909 Nobel Prize in physics by inventing a working wireless radio that functions between Canada and England.
- 1925: John Baird demonstrates the transmission of moving pictures at Selfridges, a London’s departmental store which conveniently sells couches.
- 1929: The BBC makes the first experimental TV broadcast.
- 1940: George Stibitz makes the first computer transmission using a mainframe system and remote terminals. Mammoth mainframes dominate the emerging industry through the next two decades.
- 1960: Computer geeks start experimenting with packet switching, bypassing the mainframe to send large packets of data directly to different computers.
- 1969: The first network – just 4 modes – is in operation.
- 1970: Scientists at Corning Glass Works produce the first viable optical fiber, ushering in a new era in telecommunications and enabling the internet.
- 1978: The first international packet switched network connects the U.S. and Europe.
- 1989: While working for CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, Sir Tim Berners-Lee and Robert Cailliau invent the web.
- 1990: Fledgling micro-networks slowly merge to become the behemoth that today we call the “net.â€
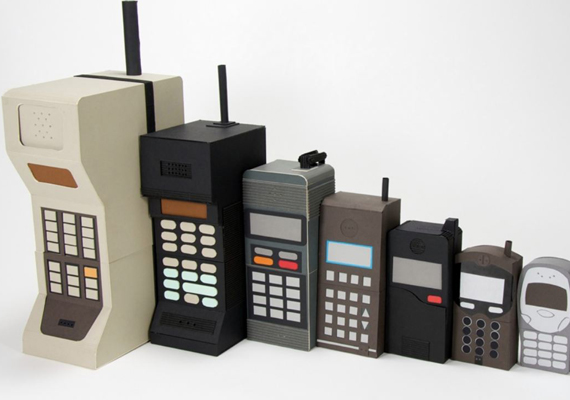
And today its 2017, the path from discovery to implementation and production moves literally at the speed of light.
(Visited 45 times, 1 visits today)
|







No comments!
There are no comments yet, but you can be first to comment this article.